Water-Channel-Integrated Earth-Air Heat Exchanger (WCIEAHE) System
2016-2018
Context
The global emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency is driving innovation in low-energy and low-carbon HVAC systems, especially in agriculture where energy consumption can be significant due to climate control and irrigation needs. In regions with humid and variable climates, there is a pressing need for HVAC solutions that reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions while maintaining optimal conditions for crop growth. This project proposes a novel approach using a water-channel-integrated earth-air heat exchanger (WCIEAHE) system in agricultural greenhouses. By leveraging groundwater energy, the system aims to precondition outdoor air, optimize irrigation, and recharge the aquifer, creating a sustainable cycle of groundwater use.
Content
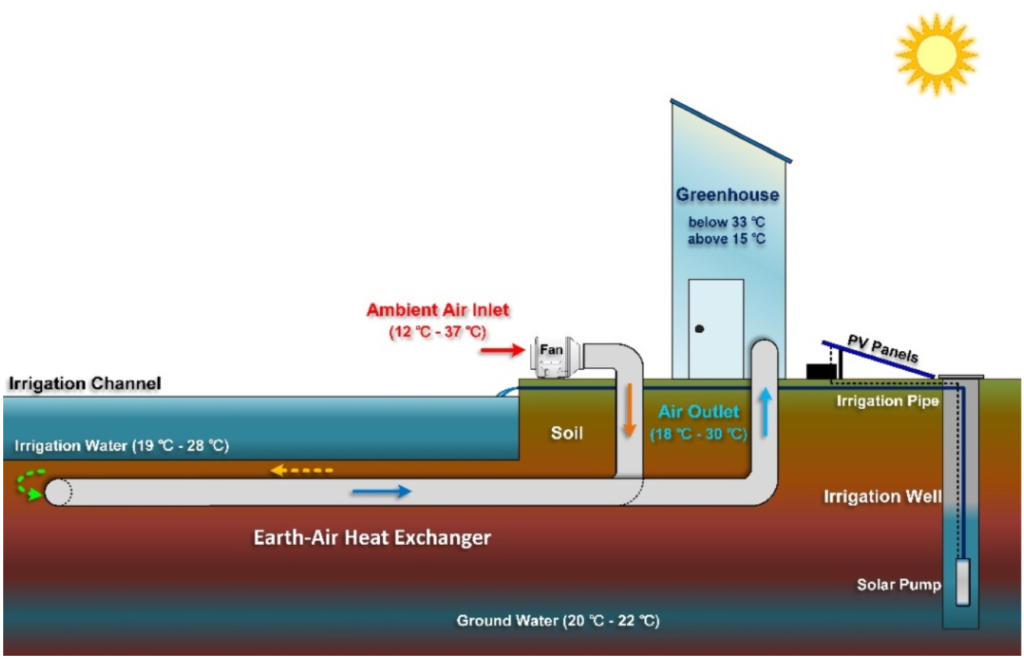
We implemented a sustainable HVAC system for agricultural greenhouses by integrating a water-channel-integrated earth-air heat exchanger. The system uses groundwater to precondition incoming air, reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions. Key features include:
- Groundwater Utilization: A solar-powered pump circulates groundwater to enhance thermal capacity and act as a thermal storage medium.
- Heat Exchange: Pipes immersed in water exchange heat with incoming air, pre-cooling and dehumidifying it before it enters the greenhouse.
- Dual Purpose: The conditioned air optimizes crop growth, and the used groundwater is directed for irrigation, eventually recharging the aquifer.
This innovative approach leverages renewable energy to sustainably optimize agricultural practices.
Conclusion
The water-channel-integrated earth-air heat exchanger system offers a sustainable, energy-efficient solution for agricultural greenhouse HVAC and irrigation needs. By utilizing groundwater for both air conditioning and irrigation, the system significantly reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions. The innovative design ensures efficient heat exchange and optimal water use, while the ability to recharge the aquifer enhances environmental sustainability. This approach aligns with global goals to reduce carbon footprints and promote renewable energy sources, exemplifying a forward-thinking integration of renewable resources into agricultural practices. The system sets a new benchmark for sustainable agriculture, contributing to environmental stewardship and energy conservation.